(repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation)
Neuromodulation
Neuromodulation refers to the process of altering or regulating nerve activity using electrical, magnetic, or chemical stimulation to modulate the nervous system’s function. Neuromodulation works by influencing the activity of neurons and neurotransmitter systems in targeted regions. It can inhibit or stimulate neurons to correct dysfunction or reduce symptoms of a disorder. It is a broad term used in medical treatments that target the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) and the peripheral nervous system (nerves outside the brain and spinal cord), aiming to treat various neurological conditions and disorders.

Common Types of Neuromodulation:
- Neurofeedback: A non-invasive brain training technique using real-time EEG monitoring to help individuals learn to self-regulate brainwave patterns for improved mental function.
Cranial Electrotherapy Stimulation (CES): Delivers low-level microcurrents to the head to alleviate symptoms of anxiety, depression, and insomnia.
Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (tDCS): Applies gentle electrical currents via scalp electrodes to modulate brain activity and support cognitive and emotional recovery. - Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS): Uses focused magnetic pulses to stimulate underactive brain regions, often used to treat depression, anxiety, and OCD.Vagus
- Nerve Stimulation (VNS): Stimulates the vagus nerve to regulate mood, inflammation, and autonomic nervous system function—especially beneficial in depression and epilepsy.
- Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS): A surgically implanted device delivers continuous electrical impulses to targeted brain areas involved in mood, movement, and behavior regulation. DBS is FDA-approved for movement disorders and under investigation for treatment-resistant depression and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)
Benefits of Neuromodulation:
- Reduces symptoms of depression, anxiety, PTSD, and OCD
- Enhances attention, memory, and cognitive processing
- Promotes emotional regulation and stress resilience
- Supports neuroplasticity and nervous system balance
- Complements traditional psychiatric care, often reducing the need for medications
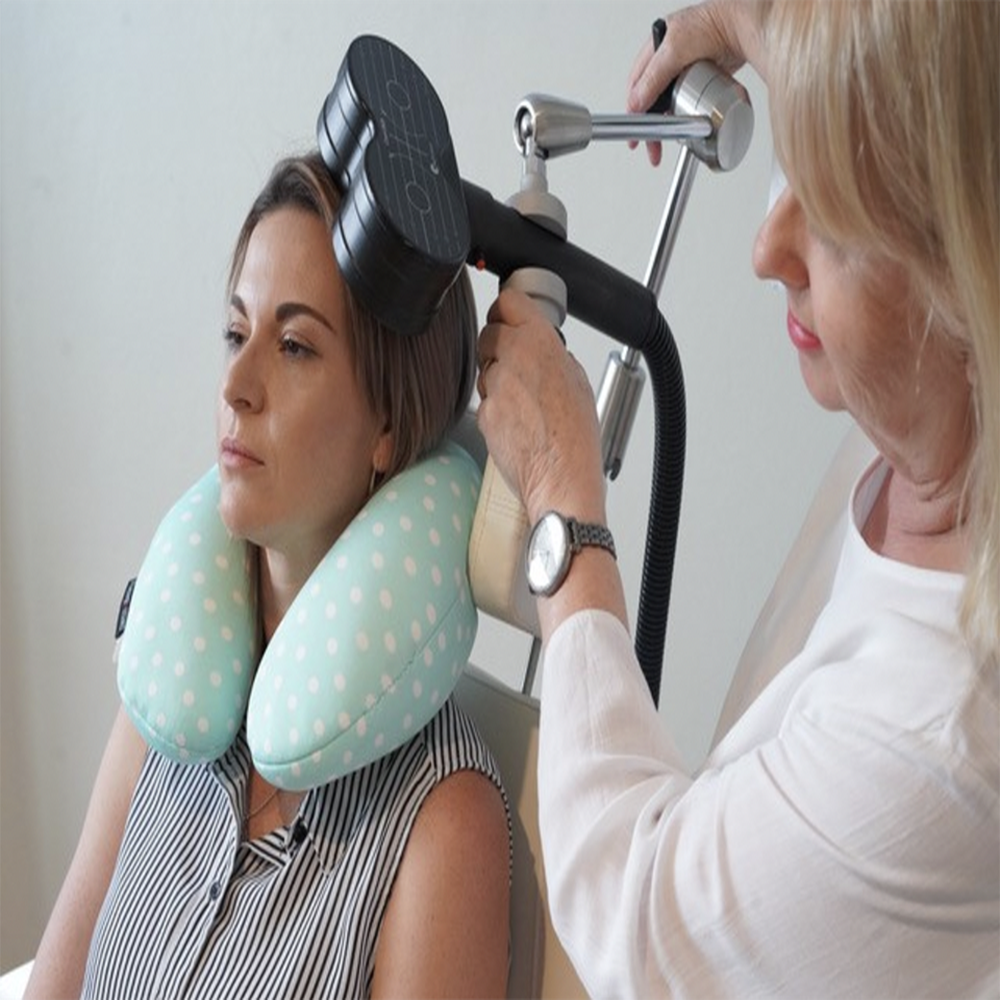
Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (rTMS) with Apollo
Repetitive Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (rTMS) is an FDA-cleared, non-invasive brain stimulation therapy used to treat depression, anxiety, PTSD, and other mental health conditions. It works by delivering focused magnetic pulses to specific regions of the brain involved in mood regulation, helping to restore healthier patterns of brain activity.
At New Image Wellness, we offer an advanced, personalized form of rTMS using the Apollo TMS System—a next-generation technology known for its precision, comfort, and optimized stimulation protocols. The Apollo system allows for customized treatments based on individual neurophysiological markers, improving both efficacy and patient experience.
How It Works:
- A magnetic coil is placed gently on the scalp, targeting key areas like the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, which is often underactive in depression.
- Pulses are delivered in repeated sessions over several weeks to encourage neuroplasticity—the brain’s ability to reorganize and form new, healthier connections.
- Over time, this helps normalize brain circuits, reduce emotional reactivity, and support long-term mental wellness.
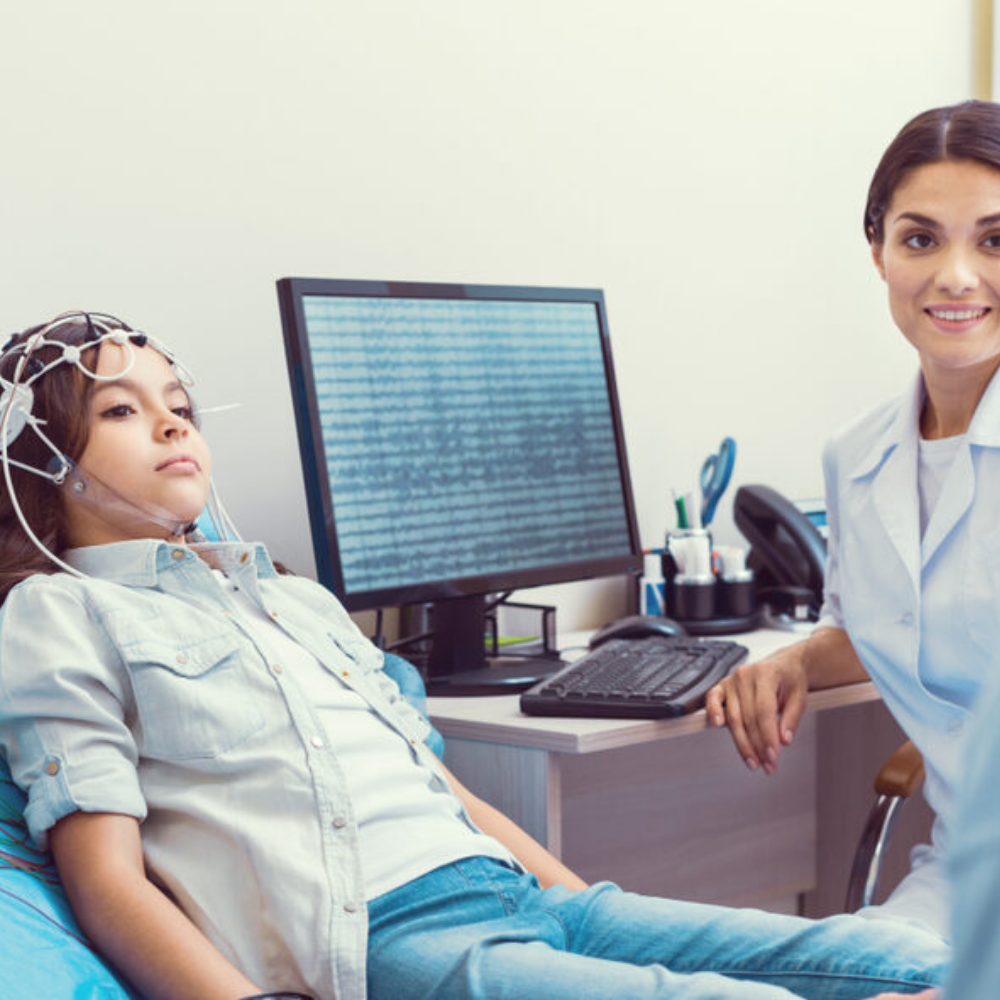

Why rTMS with Apollo?
- Personalized protocol optimization using real-time EEG-guided feedback
- More efficient sessions with accelerated theta burst or high-frequency options
- Non-invasive and drug-free, with minimal side effects
- Clinically proven to improve treatment-resistant depression and anxiety
- Comfortable, quiet, and performed in-office with no downtime

rTMS with Apollo is an ideal option for those who have not found relief through medication alone, or who seek a natural and targeted way to improve brain health and emotional balance. As part of a comprehensive integrative treatment plan, rTMS can help unlock lasting transformation in mood, cognition, and quality of life.
Neuromodulation is an evidence-informed, precision-based therapy used in integrative neuropsychiatric and functional medicine approaches. It is especially helpful for individuals who have not responded fully to medications or talk therapy alone.

What is MeRT and How does MeRT works?
MeRT stands for Magnetic e-Resonance Therapy, a therapy that is used to treat Autism, Depression, PTSD, TBI, and a wide range of other issues that stem from brain activity imbalances. Dr. Winfrey uses gentle magnetic stimulation to enhance neurological development and help the brain to heal and open pathways.
MeRT treatment starts with an evaluation that uses sophisticated brain imaging to locate the areas of the brain that are not communicating. Then we create a customized treatment of gentle magnetic waves specifically for your brain patterns. We stimulate those parts of the brain and encourage them to start communicating again. The treatment uses no drugs or medications and is completely non-invasive. And, in some instances, results have been astonishing.
An Overview of MeRT Treatment
Neuromodulation for Brain Function & Mental Health
Neuromodulation is a state-of-the-art therapeutic approach that modifies nervous system activity by delivering targeted electrical or magnetic stimulation to specific regions of the brain or nerves. These interventions help restore balance to dysregulated neural circuits, enhancing brain function and improving symptoms in a wide range of psychiatric and neurological conditions.
Neuromodulation works by influencing the brain’s electrical and chemical signaling, promoting neuroplasticity and more efficient communication across neural networks. This leads to improved mood, attention, cognitive clarity, emotional regulation, and overall mental well-being.

The 3 Components of MeRT
MeRT, or Magnetic e-Resonance Therapy, uses a three-part protocol that measures, analyzes, and improves brain function. The three part are:
qEEG
(quantitative electroencephalogram)
This non-invasive test is also called “brain mapping”. We simply place a cap on your head to map your unique brainwaves.
EKG/ECG
(electrocardiogram)
While performing the qEEG, we also use an EKG to measure your hearts electrical signals. This provides the most accurate results possible.
rTMS
After analyzing your results and developing your tailored program, we place magnetic coils along your scalp to stimulate targeted brain areas.
Testing
Your first visit includes two painless, in-office tests: a qEEG to measure brain activity and an EKG to check your heart’s electrical signals. Using this data, we create a personalized treatment plan and schedule your assessment period.
Consultation
Once we review your test results, you’ll meet one-on-one with Dr. Winfrey—virtually or in person—to go over your results, treatment plan, and next steps. We’ll answer any questions you have about the process.
Assessment Period
For two weeks, you’ll receive daily weekday treatments. On the second Friday, we repeat your EEG to track progress. If results are positive, additional two-week treatment blocks are scheduled. Progress is checked every two weeks, and most patients see lasting improvement within 4–8 weeks.
Gentle magnetic waves stimulate areas of the brain that are not communicating well with a targeted frequency specifically based on your needs. MeRT, or Magnetic e-Resonance Therapy, is a breakthrough technology that empowers doctors to analyze your brainwave data and provide targeted treatment to give you the best possible outcome. The magnetic waves used are tailored to exact parts of your brain and exact frequencies that help your brain open up areas that need support.
How does MeRT do this, exactly? Well, it starts with how the brain works.
Your brain is composed of approximately 100 billion neurons. These neurons interact with each other through brain waves, or tiny electrical oscillations, to control how your brain functions.
Your neurons can be disrupted by internal or external forces, causing brain dysfunction. Some of these forces can include:
- Trauma to the head such as a concussion
- Post-traumatic stress disorder
- Major Depressive Disorder
- Developmental disorders such as Autism, ADD, and ADHD
- Illness or disease such as stroke or Parkinson’s Disease
- Drug or alcohol addiction
- Learning disorders
- Dementia
- Multiple sports injuries (head hits)
- Anxiety
- Sleeping disorders
- Congenital issues
These disruptions can be minor or significant. Everyone has different levels of tolerance. Some people still function in day-to-day activities, while others are to some degree debilitated and lose their quality of life. MeRT attempts to reprogram these abnormal electrical signals in the brain. By identifying where your brain waves are not properly communicating, we can help to restore optimal function. MeRT technology can reshape the activity in your brain, regardless of what caused the dysfunction. Patients have reported results that they consider nothing short of miraculous.
*** Results are based on active and strict observation of our regimens. Results may vary based on the individual user and are not guaranteed.***
